Minneapolis ends talks with police union in wake of Floyd case
The police chief says ‘we will have a police department that our communities view as legitimate, trusting’.
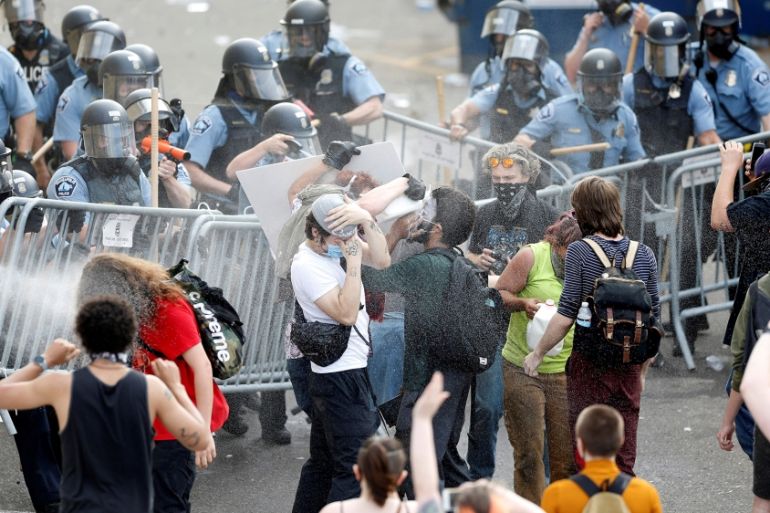
The Minneapolis Police Department will withdraw from police union contract negotiations, MPD Chief Medaria Arradondo said on Wednesday as he announced the first steps in what he said would be transformational reforms to the agency in the wake of George Floyd’s death.
Arradondo said a thorough review of the contract is planned. He said the contract needs to be restructured to provide more transparency and flexibility for true reform. The review would look at matters such as critical incident protocols, use of force, and disciplinary protocols, including grievances and arbitration.
Keep reading
list of 3 items‘Justice for George Floyd’: US protests in pictures
What happened the day George Floyd died in police custody?
He said it is debilitating for a chief when there are grounds to terminate an officer and a third-party mechanism works to keep that person on the street.
“This work must be transformational, but I must do it right,” Arradondo said of changes to the department.
He also promised new research and strategies to spot and intervene with problem officers.
“We will have a police department that our communities view as legitimate, trusting and working with their best interests at heart,” he said, adding that the department has to address issues of racism head-on.
Arradondo sidestepped a question about whether he thought union head Bob Kroll, often seen as an obstacle to reforms, should step down. He also did not directly answer a question about whether citizens should worry about a slowdown in police response time as a pushback against attempts to transform the department. Some city council members have said in the past that their wards saw such slowdowns when they complained about the police action.
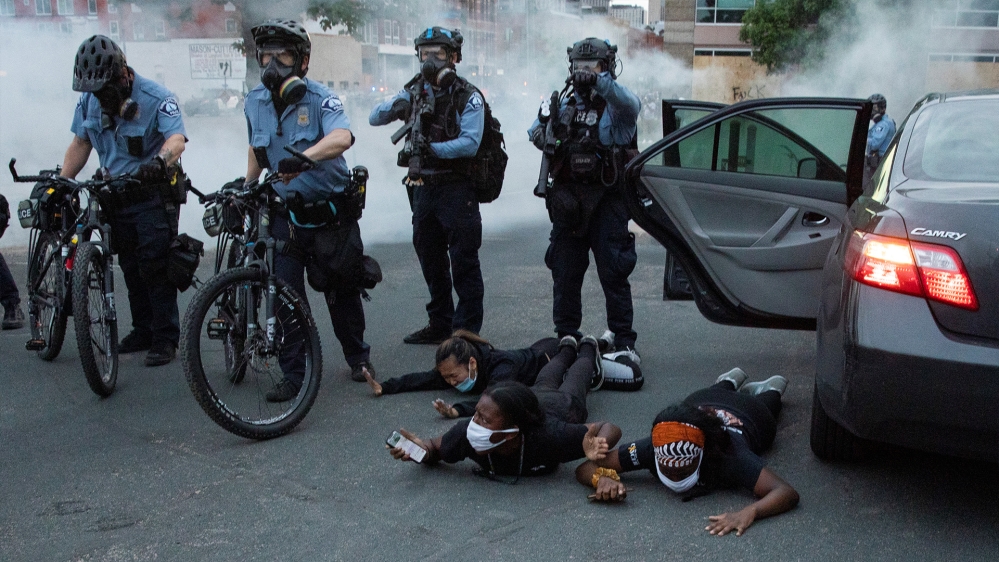
Arradondo fired the four officers involved in Floyd’s death even before they were criminally charged. A majority of Minneapolis City Council members have called for dismantling the police department, but they provided no clear plan on how that would happen.
Mayor Jacob Frey said he would not support abolishing the department, but he would favour a cultural shift in how it functions. He did not get into specifics, but told the Good Morning America show on Monday that the city has difficulty terminating and disciplining officers because of the police union.
Former police chief Janee Harteau said she received pushback from the union when she was trying to make changes.
Bob Bennett, a lawyer who said he has sued the department “hundreds” of times over police misconduct allegations, has said the union has more sway over police conduct than chiefs do.
Arradondo, the city’s first African American police chief, joined the Minneapolis Police Department in 1989 as a patrol officer, eventually working his way up to precinct inspector and head of the Internal Affairs Unit, which investigates misconduct allegations against officers. Along the way, he and four other Black officers successfully sued the department for discrimination in promotions, pay and discipline.
|
|
He was promoted to assistant chief in early 2017, then became chief later that year, after his predecessor was fired for the way she handled the fatal police shooting of a Justine Ruszczyk Damond, an Australian native who had called 911 to report a possible sexual assault behind her home.
Many hoped Arradondo could change the culture of a department that critics said too frequently used excessive force and discriminated against people of colour. Arradondo spoke of restoring trust during his swearing-in ceremony and made some quick changes, including toughening the department’s policy on the use of body cameras. But critics have continued to call for more change.