As Russia-Ukraine crisis ramps up, Biden faces sanctions dilemma
US policymakers appear united on need to oppose Russian invasion, but disagreements emerge on pace of sanctions.

Washington, DC – Russian President Vladimir Putin’s decision to recognise two breakaway regions in eastern Ukraine as independent and send troops to the territories has drawn widespread rebuke as a major escalation and a breach of international law.
But in the United States, where President Joe Biden has started imposing sanctions on Russian banks and “elites”, there is no clear consensus on how the government should respond to the Russian move.
Keep reading
list of 3 itemsUkraine crisis: What does Belarus have to gain, and lose?
Russia Moves on Ukraine | Start Here
Hawkish lawmakers are calling for the most serious US sanctions to be unleashed now, while others argue that Washington should hold on to the most severe penalties to deter potential further aggression by Moscow.
Matthew Pauly, an associate professor of history at Michigan State University, said incremental sanctions “might be sensible because such an approach would create a sliding penalty scale and offer a disincentive for future, more expansive Russian moves”.
But gradual penalties come with their own set of problems, Pauly said.
“Incremental sanctions might also invite Russia to test Ukrainian and Western resolve in stages, in hope of fracturing Kyiv’s support,” he told Al Jazeera in an email earlier this week. “The application of ‘massive,’ comprehensive sanctions now might remove a deterrent to a full-scale Russian war against Ukraine.”
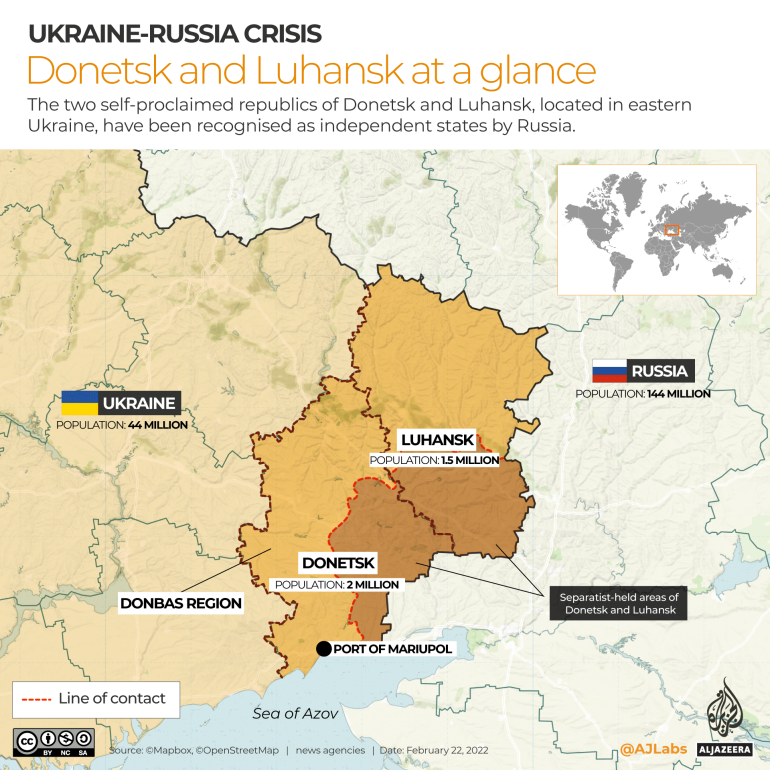
For now, Biden seems to favour gradual sanctions. On Monday, after Putin recognised the self-proclaimed Donetsk People’s Republic (DPR) and Luhansk People’s Republic (LPR), Washington imposed measures targeting trade in the two territories.
The following day, Biden announced sanctions against two Russian banks, the country’s sovereign debt and several individuals described as part of Putin’s inner circle. “If Russia goes further with this invasion, we stand prepared to go further as with sanctions,” Biden said on Tuesday.
Still, some Congress members are calling for tougher penalties against Russia now.
Republican Senator Tom Cotton called for “punishing sanctions” on Russia’s oil and gas sector and on critical industries, while key Republican Senator Lindsey Graham called Biden’s sanctions “woefully inadequate”.
“I will continue to try to work with the Biden Administration and Senate Democrats to create crippling sanctions for Putin’s invasion,” the senator wrote on Twitter on Wednesday. “However, at every turn it seems Biden Administration is being caught flat-footed.”
But Alexandra Vacroux, executive director of the Davis Center for Russian and Eurasian Studies at Harvard University, said Tuesday’s measures were “appropriate”.
“The administration needs to leave something in its pocket with which to punish Russia further if it seizes Kyiv, for example, or if it launches an invasion from three sides around the country,” Vacroux told Al Jazeera in a phone interview.
Russia has been amassing troops at Ukraine’s borders for months, sparking fears that it may be preparing a full-scale invasion of its neighbour. Moscow has denied that it plans to invade, insisting that it has legitimate security grievances relating to Kyiv’s deepening alliance with the West – and demanding guarantees that Ukraine will not be allowed to join NATO.
Numerous rounds of talks between Russian, European and American officials have failed to defuse the tensions. On Tuesday, US Secretary of State Antony Blinken cancelled a meeting with his Russian counterpart Sergey Lavrov, which was set to take place in Geneva later this week.
Meanwhile, the autonomy or independence of the eastern Ukrainian regions, where Russia-backed separatists have been battling government forces since 2014, is a separate – but not unrelated – issue. The violence previously had been handled through the Minsk Agreements and talks involving Moscow, Kyiv, Paris and Berlin.
While analysts see some legitimacy in Russia’s concern about NATO’s eastwards expansion into former Soviet republics, they say an invasion of Ukraine is illegal and cannot be justified under international law. Moreover, Ukrainian officials say Putin’s recognition of Donetsk and Luhansk as independent effectively killed the Minsk Agreements that aimed to end the fighting.
But in a speech on Monday, Putin voiced grievances that went well beyond NATO or eastern Ukraine. The Russian president went as far as questioning Ukraine’s right to exist as an independent state.
Melvyn Levitsky, professor of international policy at the University of Michigan, said Putin has put his country in an “untenable position”.
“An invasion would put Russia in the position of an outlaw or rogue country, rather than restore Russia’s position as a world leader,” Levitsky, a former career diplomat, told Al Jazeera in an email on Monday.
For now, Biden has promised to defend NATO countries with which the United States has a collective defence pact under Article 5 of the alliance. But Ukraine is not a NATO member, so US and European leaders have only threatened Russia with sanctions and isolation to dissuade it from invading.
On Tuesday, Germany halted the approval of Nord Stream 2, the Russian-owned $11bn gas pipeline across the Baltic Sea – a move that was lauded by Biden. But some US lawmakers want the project permanently scrapped – not just suspended. The US announced its own sanctions against the pipeline on Wednesday.
On Monday, former US ambassador to Ukraine John Herbst called Russia’s recognition of the independence of the two Ukrainian breakaway regions a “major escalation”, urging the Biden administration to start imposing serious sanctions on Moscow.
Herbst, who now serves as senior director of the Atlantic Council’s Eurasia Center, told Al Jazeera at that time that if Washington does not start unrolling tough sanctions, it would be making the “same mistake” as in 2014, when Putin annexed Ukraine’s Crimean Peninsula.
“The question now is whether this is simply the latest escalation in a crisis that’s going to end soon, or if this is an escalation, which would be followed by more provocative actions. And we don’t know the answer to that,” Herbst said.